- Article
Population Structure and Growth Dynamics of the Invasive Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus in the Loukkos Estuary (Morocco)
- Feirouz Touhami and
- Hocein Bazairi
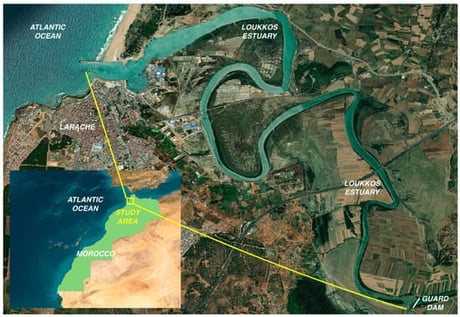
This study provides the first insights into the biology of the blue crab Callinectes sapidus in the Loukkos Estuary, based on 461 individuals collected between December 2022 and November 2023. Results indicate a well-structured invasive population. Carapace width ranged from 52 to 201 mm (mean ± SD: 121.7 ± 25.4 mm) and total weight from 12 to 512 g (128.2 ± 76.6 g). Morphometric analyses revealed pronounced sexual dimorphism, with males larger and heavier than females. Size structure shifted seasonally, with smaller crabs dominating spring–summer samples and larger crabs in winter. Biometric relationships were significant and indicated negative allometric growth in both sexes. The sex ratio was strongly male-biased (M/F = 2.72). Condition factor varied with season and sex, peaking in summer and reaching minima in autumn. Female maturity exhibited marked seasonality: immature females prevailed from spring to autumn, whereas mature females occurred mainly in winter. Logistic modeling estimated size at 50% maturity (L50) at 126.7 mm carapace width in females. Results suggest that Loukkos Estuary functions primarily as a nursery and growth area for C. sapidus and provide essential baseline information for future monitoring and management of this invasive species.
18 February 2026